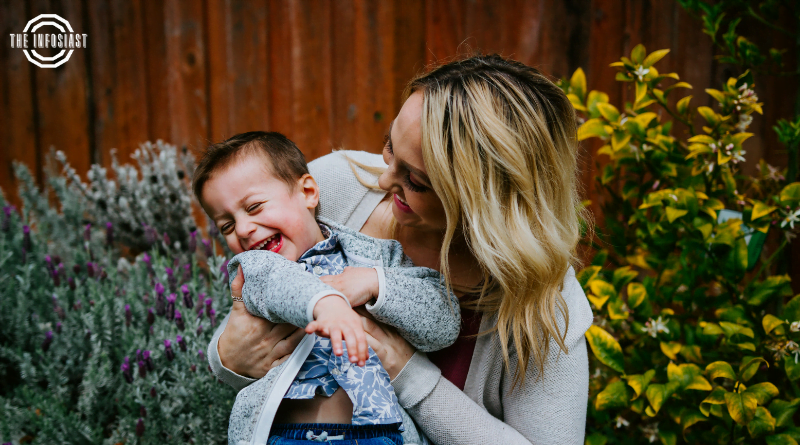
Matrilineality, an intriguing kinship system, traces ancestry and inheritance through the maternal line. This unique cultural practice challenges conventional patrilineal norms, and its historical significance persists in various societies around the world. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the concept of matrilineality, its implications on family dynamics, and how it continues to shape cultural identities today.
Understanding Matrilineality:
Matrilineality is a social structure in which lineage, inheritance, and kinship are traced through the mother’s line. Unlike patrilineal systems, which emphasize the father’s lineage, matrilineality centers on the maternal ancestors.
Historical Origins of Matrilineality:
Matrilineal practices have ancient origins and can be traced back to several indigenous cultures, such as the Minangkabau of Indonesia and the Akan people of Ghana. These societies preserved matrilineal traditions as a way to honor women’s roles and contributions.
Family and Clan Ties:
In matrilineal societies, family identity and membership in clans or tribes are determined through the maternal line. Inheritance, property rights, and social standing often follow the matrilineal lineage.
Empowering Women:
Matrilineality has been recognized as a system that empowers women within their communities. In matrilineal societies, women often hold positions of authority and play essential roles in decision-making processes.
Matrilineal Inheritance and Property Rights:
In matrilineal systems, property and wealth are typically passed down through the maternal line. This practice contributes to women’s economic independence and influence within the family structure.
Matrilineality and Cultural Identity:
Matrilineal heritage is an essential aspect of cultural identity in certain communities. It influences traditional customs, rituals, and artistic expressions, reflecting the deep-rooted connection to maternal ancestry.
The Role of Men in Matrilineal Societies:
While matrilineality centers on the mother’s line, men still play significant roles in matrilineal societies. They may be involved in childcare, communal decision-making, and participating in rituals and ceremonies.
Matrilineality in Modern Context:
While some traditional matrilineal societies have seen changes due to external influences, aspects of matrilineal heritage continue to be preserved and celebrated by communities worldwide.
Challenges and Adaptations:
Matrilineal societies may encounter challenges in preserving their traditions amidst modernization and globalization. However, communities often find ways to adapt while maintaining the essence of their matrilineal heritage.
Matrilineality as Cultural Diversity:
Understanding and appreciating matrilineality as part of cultural diversity enriches our global perspective. Embracing and respecting different kinship systems fosters inclusivity and respect for cultural heritage.
Matrilineality is a captivating cultural practice that places emphasis on maternal ancestry and kinship. Understanding the historical origins, family dynamics, and significance of matrilineal systems offers insights into diverse cultural identities. By acknowledging and valuing matrilineality’s unique heritage, we can foster a more inclusive and appreciative global community. Embracing the diverse kinship systems that shape our world enriches our understanding of human history and cultural traditions, promoting respect and harmony across societies.