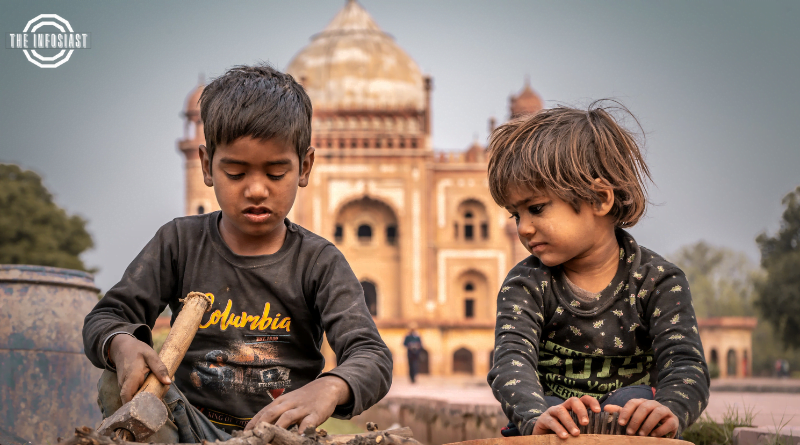
Dalit, a term commonly used in South Asia, refers to a historically marginalized and oppressed social group. Understanding the challenges faced by Dalits and promoting awareness about their rights and struggles are essential steps towards fostering inclusivity and social justice. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the concept of Dalit, explore their historical context, and advocate for solutions to address the issues faced by this community.
Defining Dalit:
The term “Dalit” comes from the Sanskrit word “dal,” which means broken or oppressed. It is used to describe individuals belonging to socially disadvantaged castes in South Asia, often experiencing discrimination and social exclusion.
Historical Context:
The origins of Dalit discrimination can be traced back to the caste system, a hierarchical social structure prevalent in South Asia for centuries. Dalits were historically assigned the lowest caste and were subjected to various forms of social, economic, and political oppression.
Social and Economic Challenges:
Dalits have faced significant challenges in accessing basic rights, education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. Discrimination and segregation persist in many areas, hindering their social and economic mobility.
The Struggle for Equality:
Over the years, Dalit activists and social reformers have fought against caste-based discrimination, advocating for social justice and equal rights. Their efforts have led to important legislative changes, but the struggle for full equality continues.
Empowering Dalit Voices:
Promoting awareness about Dalit issues and amplifying their voices is crucial for fostering inclusivity and social change. Highlighting Dalit achievements and contributions can challenge stereotypes and promote positive narratives.
Dalit Art and Culture:
Dalit communities have rich cultural traditions, including art, music, and literature that reflect their experiences and resilience. Recognizing and appreciating Dalit art can contribute to preserving cultural heritage and promoting diversity.
Breaking Barriers through Education:
Education plays a pivotal role in empowering marginalized communities like Dalits. Initiatives that promote access to quality education and scholarships can uplift Dalit youth and pave the way for a more inclusive society.
Addressing Economic Disparities:
Creating economic opportunities and promoting entrepreneurship among Dalit communities can help address economic disparities and foster sustainable development.
Allyship and Solidarity:
Addressing Dalit issues requires collective efforts and allyship from individuals and organizations. Building bridges of solidarity can create a united front against discrimination and social injustice.
Celebrating Progress and Pushing for Change:
While progress has been made in addressing Dalit issues, there is still a long way to go. Celebrating achievements and progress while acknowledging the challenges can motivate further action and advocacy.
Understanding the complexities of the Dalit experience and advocating for their rights and equality are crucial steps towards creating a more inclusive and just society. By promoting awareness, fostering empathy, and amplifying Dalit voices, we can contribute to dismantling caste-based discrimination and promoting social change. Recognizing the contributions of Dalit communities and celebrating their resilience enriches our collective cultural heritage. Empowering Dalits through education, economic opportunities, and allyship can pave the way for a more equitable and harmonious future. Together, let us work towards a world where every individual, regardless of their background, can live with dignity, respect, and equal opportunities.