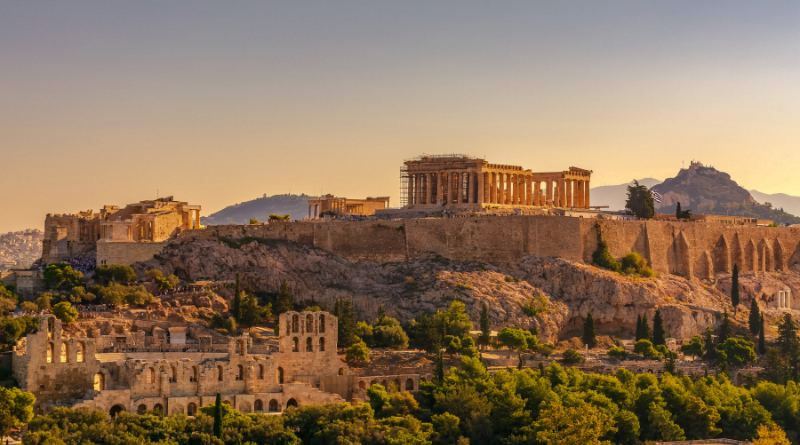
Civilization, a term that resonates with the very essence of human society, encompasses the collective achievements, culture, and development of communities throughout history. It is a rich tapestry woven with threads of innovation, culture, and progress. In this comprehensive article, we will embark on a journey through the ages to explore the concept of civilization, its evolution, and its profound impact on our world.
Defining Civilization
Let’s begin with a clear definition. Civilization refers to an advanced stage of human development characterized by complex social, cultural, economic, and political structures. It represents a level of sophistication in human organization beyond basic survival needs.
The Birth of Civilization
Civilization, as we understand it today, emerged with the Neolithic Revolution around 10,000 BCE. This transformative period marked the shift from nomadic, hunter-gatherer societies to settled agricultural communities. The birthplaces of civilization include Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley, and ancient Egypt.
The Cradle of Civilization – Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia, often referred to as the “cradle of civilization,” was home to the world’s first known cities, such as Ur and Uruk. The Sumerians, Akkadians, and Babylonians laid the foundations for governance, writing, and advanced agriculture.
Ancient Egypt – The Nile’s Gift
Along the banks of the Nile River, ancient Egypt thrived as a great civilization. The Egyptians are renowned for their monumental architecture, hieroglyphic writing, and intricate belief systems centered around gods and the afterlife.
The Indus Valley Civilization
In the Indus Valley, present-day Pakistan and northwest India, another ancient civilization flourished. The Indus Valley Civilization displayed advanced urban planning, a system of writing, and complex trade networks.
The Ancient Roots of China
China’s civilization, dating back to the Xia and Shang dynasties, showcased early advancements in writing and metallurgy. The Great Wall of China stands as a testament to ancient engineering marvels.
Greek Civilization – The Birth of Democracy and Philosophy
Ancient Greece contributed immensely to the development of Western civilization. The Greeks introduced concepts of democracy, philosophy, and rational thought through the works of philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle.
The Roman Empire – A Legacy of Governance and Engineering
The Roman Empire left an enduring legacy in governance, law, and engineering. Roman aqueducts, roads, and the concept of “civis Romanus sum” (“I am a Roman citizen”) are pivotal to Western history.
The Medieval Ages – A Flourishing of Arts and Sciences
The Medieval Ages brought the flourishing of arts and sciences in the Islamic Golden Age, the European Renaissance, and the architectural marvels of Gothic cathedrals.
The Age of Exploration and Colonization
The Age of Exploration in the 15th and 16th centuries expanded civilization’s horizons. European powers established colonies worldwide, exchanging cultures, goods, and ideas.
Modern Civilization – A Global Tapestry
Today, civilization is a global tapestry of diverse cultures, languages, and innovations. It encompasses technological advancements, social progress, and interconnected economies.
Challenges and Achievements
While civilization has brought remarkable achievements, it also faces significant challenges, including environmental sustainability, social inequalities, and geopolitical tensions. Addressing these issues is essential for the future of our global society.
Nurturing Our Collective Legacy
Civilization is a testament to human ingenuity, adaptability, and progress. It has evolved from its ancient origins to become a complex web of interconnected societies, each contributing to the shared human experience.
As we navigate the complexities of modern civilization, it is crucial to reflect on the lessons of the past, embrace cultural diversity, and work collectively to address the challenges we face. Civilization is not static; it is a dynamic force driven by the creativity and resilience of humanity.
By understanding the rich tapestry of civilization and our role within it, we can collectively shape a future that builds on the achievements of the past and fosters a more inclusive, sustainable, and harmonious world for generations to come.