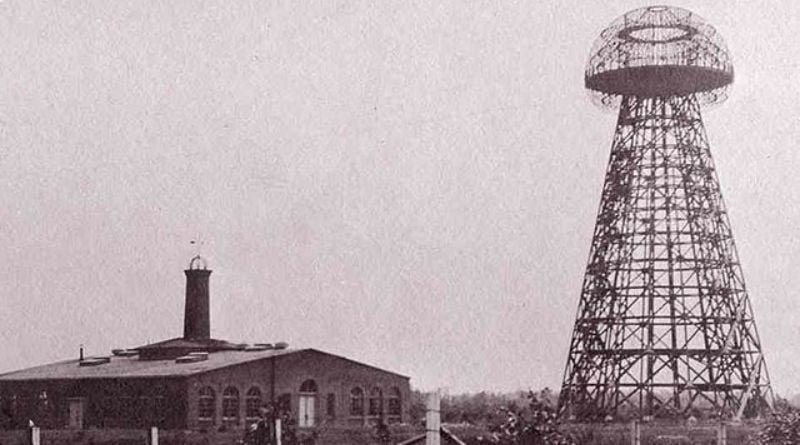
Imagine a world where electricity flows freely through the air, powering your devices without the need for wires or cables. This was the visionary dream of Nikola Tesla, a pioneer of electricity whose ideas often seemed ahead of their time. His Wardenclyffe Tower, a magnificent structure that once stood on Long Island, New York, was a central piece of this ambitious plan for wireless power transmission.
The Man Behind the Tower: Nikola Tesla and his Vision
Nikola Tesla, a Serbian-American inventor, was a captivating figure in the scientific world of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. He made significant contributions to the development of alternating current (AC) electricity, the system that powers our homes and businesses today. But Tesla’s ambitions stretched far beyond conventional power grids. He envisioned a world where electricity could be transmitted wirelessly, eliminating the need for cumbersome wires and revolutionizing communication and energy access.
The Birth of Wardenclyffe: A Tower for a Global Dream
In 1901, Tesla began construction on Wardenclyffe Tower, a 187-foot (57-meter) tall structure made of steel and concrete. The tower, located in Shoreham, New York, was designed to be a global communication and power station. Tesla believed that by using a massive Tesla coil at the top of the tower, he could transmit electrical energy and information across vast distances. His plan involved transmitting radio waves at specific frequencies that would resonate with receiving devices, inducing currents and powering them wirelessly.
Beyond Power: A Tower for Global Communication
While wireless power transmission was Tesla’s primary goal for Wardenclyffe, he also envisioned the tower as a revolutionary communication hub. He believed it could transmit messages, telephony, and even facsimile images across the Atlantic Ocean, connecting continents without the need for underwater cables. This ambition foreshadowed the development of radio and wireless communication technologies that would become commonplace in the decades to come.
The Financial Hurdles and the Unfinished Symphony
Tesla secured funding for Wardenclyffe from J.P. Morgan, a prominent financier. However, Morgan’s vision for the project differed from Tesla’s. Morgan was primarily interested in using the tower for commercial communication purposes, not wireless power transmission. As the project progressed, the financial backing dwindled due to a combination of factors, including the success of Marconi’s transatlantic radio transmission in 1901. Tesla, unable to secure further funding, was forced to abandon Wardenclyffe in 1904, leaving the tower unfinished. The incomplete structure stood as a testament to Tesla’s ambition and a symbol of his unrealized dream.
The Legacy of Wardenclyffe: A Spark for the Future
Although Wardenclyffe never achieved its full potential, its legacy continues to inspire scientists and engineers. Tesla’s ideas on wireless power transmission, though deemed impractical at the time, have gained renewed interest in recent years. Today, researchers are exploring various methods for wireless power transfer, such as inductive charging and magnetic resonance. While large-scale wireless power transmission, as envisioned by Tesla, remains a challenge, the advancements in these fields owe a debt of gratitude to his pioneering spirit.
The Technical Challenges of Wireless Power Transmission
There are several technical hurdles that hindered the success of Tesla’s Wardenclyffe project and continue to pose challenges for large-scale wireless power transmission today. Here are some key considerations:
Energy Loss: Wireless transmission inherently involves energy loss due to factors like distance and resistance. Efficiently transmitting significant amounts of power wirelessly over long distances remains a challenge.
Safety Concerns: High-powered electromagnetic fields associated with wireless power transmission could pose potential health risks. Careful design and regulation are crucial to ensure safety.
Limited Range: Current wireless power transmission technologies typically have a limited range, making them more suitable for short-distance applications like charging mobile devices.
The Future of Wireless Power: Where Do We Go From Here?
Despite the challenges, advancements in technology are paving the way for a future where wireless power transmission becomes a reality. Here are some promising areas of exploration:
Inductive Charging: This technology, already used in smartphones and other devices, utilizes magnetic fields to transfer power over short distances. Advancements in this area could lead to longer-range and more efficient wireless charging solutions.
Magnetic Resonance: This technology uses specific frequencies to create a resonant coupling between a transmitter and receiver, enabling wireless power transfer over a distance. While still in its early stages, it holds promise for powering devices at a distance.
Radio Waves: Researchers are exploring the use of high-frequency radio waves to transmit power. This method faces challenges due to energy loss over distance, but advancements in beamforming technology could improve its efficiency.
The Wardenclyffe Tower’s Impact on Modern Technology
While Tesla’s grand vision for Wardenclyffe remained unrealized, the tower’s legacy extends far beyond its physical structure. Tesla’s ideas on wireless power transmission and global communication have profoundly influenced the development of modern technology. Here are some key areas where his work continues to resonate:
Mobile Phone Charging: The concept of wireless charging for portable devices directly stems from Tesla’s principles. Today, inductive charging pads utilize the same basic principles of magnetic fields to transfer power wirelessly to smartphones and other gadgets.
Wireless Communication Revolution: Tesla’s belief in transmitting information across vast distances paved the way for the development of radio and wireless communication technologies. From radio waves to Wi-Fi and cellular networks, our ability to connect wirelessly across the globe owes a debt to his pioneering spirit.
Wardenclyffe as a Museum and a Testament to Innovation
The Wardenclyffe Tower, though unfinished, has been preserved as a museum. The Tesla Science Center at Wardenclyffe offers visitors a glimpse into Tesla’s visionary mind. Through exhibits, demonstrations, and educational programs, the museum sheds light on Tesla’s groundbreaking work, including his ideas on wireless power transmission. The site serves as a constant reminder of the importance of audacious dreams and the relentless pursuit of innovation.
The Ethical Considerations of Wireless Power
As wireless power transmission technologies advance, it’s crucial to consider the ethical implications. Here are some key questions that need to be addressed:
Accessibility and Equity: Will wireless power be accessible to all, or will it exacerbate existing inequalities in energy access?
Environmental Impact: How will the production and implementation of wireless power systems impact the environment?
Regulation and Safety: What regulations are needed to ensure the safe and responsible use of high-powered electromagnetic fields associated with wireless power transmission?
The Wardenclyffe Tower stands as a testament to Nikola Tesla’s boundless imagination and his unwavering belief in the future of wireless technology. While his dream of global wireless power transmission remains unfulfilled, his ideas continue to inspire researchers and shape the development of modern technologies. As we move towards a future with ever-increasing energy demands, the concept of wireless power holds immense potential. The story of Wardenclyffe serves as a reminder that even the most audacious dreams can spark innovation and pave the way for a more connected and sustainable future.