Civil rights represent the foundation of a just and equitable society, ensuring that every individual, regardless of race, gender, religion, or background, is treated with fairness and respect. Rooted in the principles of equality and justice, civil rights are essential for protecting individuals from discrimination and empowering them to participate fully in all aspects of life. This article delves into the history, significance, and ongoing efforts to uphold civil rights while emphasizing their role in achieving true equality.
The Evolution
Historical Overview
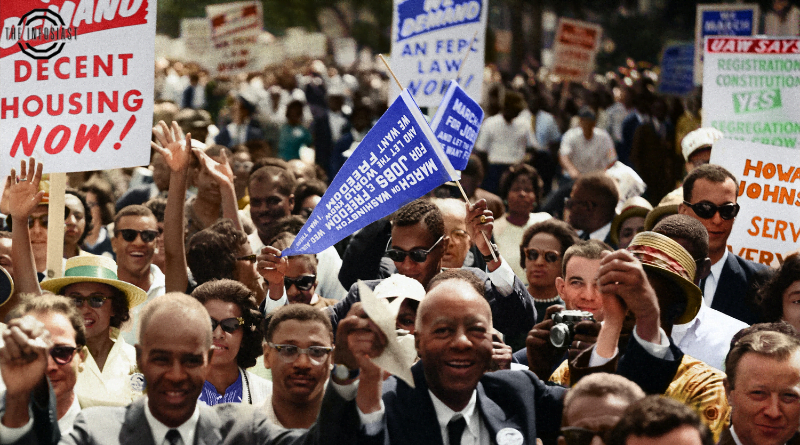
- The Civil Rights Movement in the U.S.: A pivotal era in the 1950s and 1960s aimed at dismantling racial segregation and ensuring equal rights for African Americans. Landmark events include the Montgomery Bus Boycott and the March on Washington.
- Global Movements: Civil rights struggles have also taken place worldwide, such as the anti-apartheid movement in South Africa and campaigns for women’s suffrage in the early 20th century.
Key Milestones
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948): A global affirmation of fundamental rights and freedoms.
- Civil Rights Act of 1964 (U.S.): Prohibited discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
- Equal Pay Act (1963): Addressed wage disparities, marking an important step toward workplace equality.
The Importance in Modern Society
Promoting Equality
- Eliminate Discrimination: Protect individuals from unfair treatment in employment, education, housing, and public services.
- Ensure Equal Opportunities: Provide access to resources and opportunities, fostering an inclusive society.
Strengthening Democracy
- Encouraging Civic Participation: Empowering marginalized communities to engage in democratic processes.
- Building Trust: Creating a society where all individuals feel valued and respected.
Challenges
Despite progress, significant challenges remain:
Systemic Inequality
- Racial Disparities: Persistent racial inequalities in wealth, education, and healthcare.
- Gender Inequality: Wage gaps and underrepresentation of women in leadership roles.
Legal and Policy Gaps
- Lack of Comprehensive Protections: In some regions, legal protections against discrimination remain inadequate.
- Implementation Challenges: Policies are often undermined by poor enforcement or lack of political will.
Social Resistance
Cultural biases and resistance to change can slow the progress of civil rights advancements.
Steps Toward Equality
Strengthening Legal Protections
- Comprehensive Legislation: Expanding laws to cover all forms of discrimination, including sexual orientation and gender identity.
- Effective Enforcement: Ensuring that existing policies are implemented rigorously.
Educational Initiatives
- Raising Awareness: Promoting understanding of civil rights through education.
- Empowering Individuals: Providing resources and training to help marginalized groups advocate for their rights.
Community Engagement
- Grassroots Movements: Supporting local organizations working to address inequality.
- Allies and Advocates: Encouraging individuals from all backgrounds to support civil rights efforts.
Case Studies
The Voting Rights Act (1965)
This U.S. law aimed to eliminate barriers to voting for African Americans, significantly increasing voter turnout and representation.
Gender Equality in Iceland
Iceland’s policies on equal pay and parental leave serve as a model for addressing workplace inequality.
Marriage Equality Movements
Efforts to legalize same-sex marriage worldwide highlight the ongoing expansion of civil rights protections.
The Role of Equality
Equality is the cornerstone of civil rights, ensuring fairness and inclusivity in every aspect of society:
- Economic Equality: Addressing disparities in wealth and opportunity.
- Social Equality: Challenging stereotypes and promoting respect for diversity.
- Political Equality: Ensuring all individuals have a voice in governance and decision-making.
Challenges Ahead and the Path Forward
Overcoming Resistance
- Combating Prejudice: Addressing unconscious biases through education and dialogue.
- Promoting Solidarity: Building alliances across diverse communities to support shared goals.
Leveraging Technology
- Digital Advocacy: Using social media and online platforms to raise awareness and mobilize support.
- Data-Driven Solutions: Employing analytics to identify disparities and measure progress.
Sustainable Progress
- Long-term Commitment: Ensuring that civil rights remain a priority for future generations.
- Inclusive Leadership: Promoting diversity in decision-making roles across sectors.
Conclusion
Civil rights are the foundation of a fair and just society, rooted in the principle of equality. While progress has been made, the journey toward true equality requires ongoing effort, advocacy, and collaboration. By strengthening legal protections, fostering awareness, and promoting inclusivity, we can empower individuals and communities to thrive. The path to equality is not without challenges, but the collective commitment to civil rights ensures a brighter and more equitable future for all.