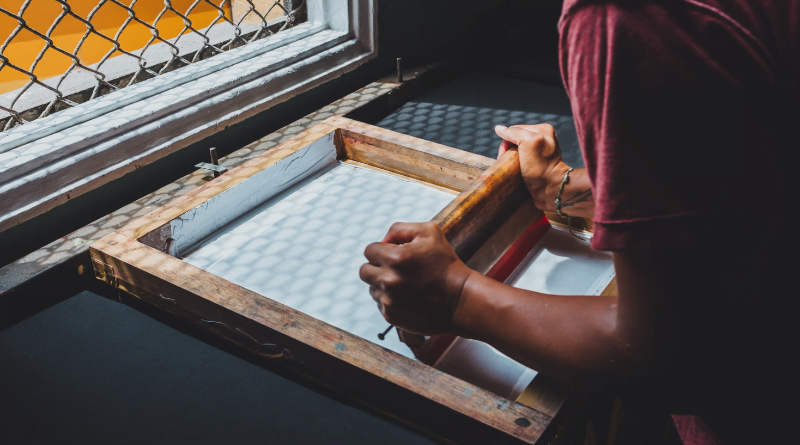
Woodblock printing has ancient roots, dating back to ancient China during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 AD). The inventor, Bi Sheng, created individual characters on clay and wood and then coated them with ink for printing. These early woodblock prints paved the way for the mass production of texts, revolutionizing the spread of knowledge in China and beyond.
The Woodblock Printing Process
1. Materials and Tools
Woodblock printing begins with carefully selected materials and tools. The key components include:
– Wood Blocks: Typically made from hardwoods like cherry, pear, or boxwood, these blocks serve as the canvas for the design.
– Carving Tools: Skilled artisans use a variety of carving tools to meticulously create the design on the woodblock. Precision is crucial to ensure the quality of the final print.
– Ink and Rollers: High-quality ink is applied to the carved woodblock using rollers. The ink must have the right consistency to achieve optimal results.
2. Design Creation
Creating a woodblock design is an art in itself. Artists carefully plan their designs and transfer them onto the woodblock. This process can be time-consuming, as even the slightest mistake can affect the final print.
3. Carving the Woodblock
Once the design is transferred, skilled artisans begin the intricate process of carving. They carefully remove the wood around the design, leaving raised areas that will receive ink for printing. This step requires precision and patience.
4. Inking and Printing
With the woodblock carved, it’s time to apply ink. A roller evenly coats the surface of the woodblock, ensuring that every detail of the design is covered. The inked woodblock is then pressed onto paper, fabric, or other surfaces, transferring the design.
5. Repeat and Refine
Woodblock printing often involves multiple blocks for different colors or layers of the design. The process is repeated for each color or layer, with meticulous alignment to create a cohesive image.
The Significance of Woodblock Printing
Woodblock printing played a pivotal role in the dissemination of information, art, and culture throughout history. Here are some key aspects of its significance:
1. Cultural Preservation
Woodblock printing was instrumental in preserving cultural and religious texts, artwork, and historical records. It allowed for the replication of sacred scriptures, classic literature, and iconic artwork, ensuring their survival through the ages.
2. Spreading Knowledge
The ability to produce multiple copies of texts and illustrations revolutionized education and the exchange of ideas. Woodblock printing made knowledge more accessible, fostering intellectual growth and innovation.
3. Artistic Expression
Artists embraced woodblock printing as a medium for creative expression. The technique allowed them to produce intricate and vibrant prints that captured the essence of their artistic visions. Famous ukiyo-e prints from Japan, for example, are treasured worldwide.
4. Cultural Exchange
Woodblock printing contributed to cultural exchange between regions. It facilitated the sharing of artistic styles, religious beliefs, and scientific knowledge, enriching societies across the globe.
Woodblock Printing in Modern Times
While modern printing technologies have largely replaced traditional woodblock printing for mass production, this art form continues to thrive as a revered craft and a source of inspiration for contemporary artists. Many artisans and printmakers still practice woodblock printing, preserving its heritage and aesthetic appeal.
Woodblock printing is a timeless art form that has left an indelible mark on the worlds of culture, knowledge, and art. Its historical significance, intricate process, and enduring appeal continue to captivate enthusiasts and artists alike. Whether you’re an art aficionado or a history buff, exploring the world of woodblock printing is a journey worth embarking on.