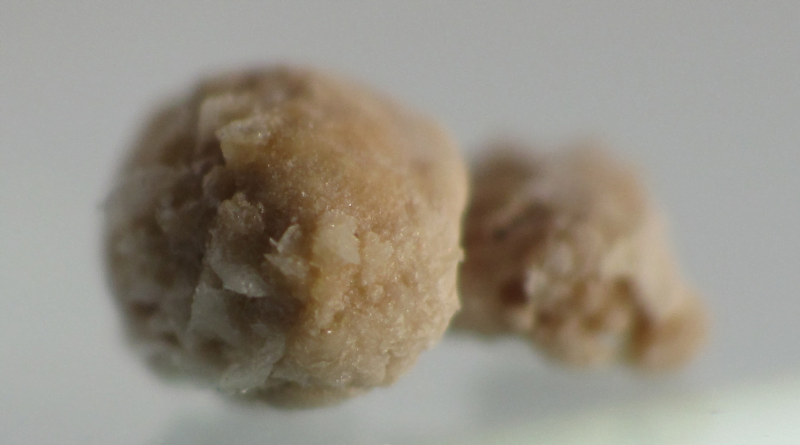
Renowned for their intricate formation, kidney stones pose a pervasive health challenge affecting millions annually. This ailment transpires as minerals and various compounds in the urine coalesce, giving rise to rigid deposits. The resultant kidney stones, fraught with intense pain, sometimes manifest in serious complications.
Intriguingly, women share an equal susceptibility to kidney stone development with their male counterparts. Yet, distinctive risk factors interweave with the female experience, notably entwined with phenomena such as pregnancy and menopause.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones in Women
A telltale sign of kidney stones manifests as an acute, undulating pain in the lower back or side. This torment, akin to rhythmic waves, may be accompanied by an array of additional symptoms:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Elevated body temperature and chills
- Pain or a burning sensation during urination
- Urine tinted pink, red, or brown
- Cloudy or malodorous urine
- Increased frequency of urination
- Urgency to urinate
- Challenges in the act of urination
- Kidney Stones and Pregnancy
Expectant mothers face an escalated susceptibility to kidney stones. The surge in hormonal production during pregnancy elevates mineral concentration in urine. Simultaneously, the expanding uterus applies pressure to the ureters, impeding urine flow and heightening the likelihood of kidney stone formation.
Symptoms echo those in non-pregnant women, with the addition of:
- Upper abdominal pain
- Groin pain
- Flank discomfort (situated between ribs and hip bone)
- Hematuria (blood in the urine)
- Elevated blood pressure
- Kidney Stones and Menopause
Post-menopausal women are also predisposed to kidney stones. The decline in estrogen post-menopause initiates urinary tract alterations. Furthermore, menopausal women may harbor additional risk factors like osteoporosis and hypertension.
Symptoms in menopausal women mirror those of their non-menopausal counterparts, with notable distinctions:
- Painful intercourse
- Loss of bladder control
- Increased frequency and urgency of urination
- When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Should symptoms suggestive of kidney stones emerge, prompt medical consultation is imperative. These stones harbor the potential for severe complications, encompassing infections and renal impairment.
Treatment Modalities for Kidney Stones
The treatment trajectory hinges on stone size and location. While diminutive stones may autonomously traverse with analgesics and ample fluids, larger stones or those instigating complications may necessitate surgical intervention.
Mitigating the risk of kidney stones can be achieved through various proactive measures:
- Adequate fluid intake, with a focus on water
- Adoption of a sodium-restricted, fiber-rich diet
- Abstinence from sugary beverages
- Maintenance of a healthy body weight
- Regular engagement in physical exercise
Kidney stones, a pervasive and agonizing ailment, impartially affect both genders. However, women face heightened susceptibility during pivotal life stages such as pregnancy and menopause. In the event of symptomatic presentation, swift medical intervention is pivotal. Proactive measures, including hydration, dietary considerations, and regular exercise, can significantly deter the formation of kidney stones.
Real-life Narratives and Instances
Sarah’s Story: A 35-year-old woman traversing the second trimester of her pregnancy, Sarah encountered excruciating pain in her right flank. The severity of her suffering prompted an emergency room visit, culminating in a kidney stone diagnosis. Hospitalized for observation, Sarah underwent pain management and fluid therapy, facilitating the stone’s eventual passage and her return home.
Mary’s Experience: A menopausal woman in her mid-fifties, Mary encountered intermittent pain in her lower back and side, coupled with nausea and vomiting. Seeking medical attention, Mary received a kidney stone diagnosis. Although initial attempts at passage with pain management and fluids proved futile, surgical intervention became imperative for stone removal.