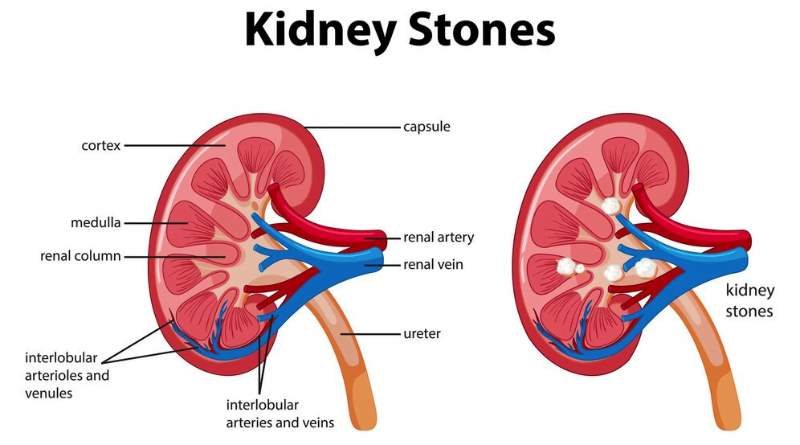
Kidney stones, those rigid formations that materialize within the renal structures, can induce agonizing pain and unease. Although their impact can befall anyone, a hereditary inclination for kidney stones prompts the inquiry: Is the transmission of kidney stones a hereditary affair?
Indeed, there exists a hereditary facet to kidney stones. Investigations reveal that individuals with a familial background of kidney stones possess a heightened susceptibility to their development. This intimates that particular genes might exert influence in elevating an individual’s predisposition to the formation of kidney stones.
Scientists have pinpointed myriad genes that may contribute to the genesis of kidney stones. These genes are implicated in processes such as:
• Urine composition: Certain genes influence the levels of minerals and salts in urine, thereby impacting crystal formation.
• Urine acidity: The pH of urine can also sway crystal formation, with certain genes dictating the body’s proficiency in regulating urine pH.
• Renal transport: Genes involved in the transport of substances to and from the kidneys can likewise partake in the formation of kidney stones.
Heritage Configurations of Kidney Stones
The precise heritage configuration of kidney stones remains not wholly comprehended, yet it likely embodies a complex trait involving a multiplicity of genes. This conveys that while a familial history heightens the susceptibility, it doesn’t unequivocally ensure that an individual will manifest kidney stones.
Despite the genetic influence, environmental constituents also contribute to the formation of kidney stones. These encompass:
• Diet: A diet abundant in oxalate, salt, and animal protein can escalate the vulnerability to kidney stones.
• Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can intensify urine concentration, fostering crystal formation.
• Specific medical conditions: Ailments like urinary tract infections, obesity, and hyperparathyroidism can augment the risk of kidney stones.
Even in the presence of a familial chronicle, there are measures one can adopt to mitigate the risk of developing kidney stones:
• Pursue a wholesome diet: Curtail the consumption of foods rich in oxalate, restrict salt intake, and moderate animal protein.
• Ensure adequate hydration: Strive to consume ample fluids, particularly water, to uphold urine dilution.
• Sustain a healthy weight: Excessive weight or obesity amplifies the susceptibility to kidney stones.
• Regulate underlying medical conditions: Effectively manage conditions like diabetes and hypertension to diminish the overall risk of kidney stones.
In the event of a family lineage with kidney stones or the manifestation of symptoms, consult with your medical practitioner. They can evaluate your risk factors and advocate appropriate preemptive measures or treatment modalities.
While kidney stones possess a genetic dimension, environmental elements wield substantial influence in their genesis. By embracing salubrious lifestyle habits and addressing foundational medical conditions, one can efficaciously curtail the risk of incurring these troublesome stones and safeguard the overall well-being of the kidneys.