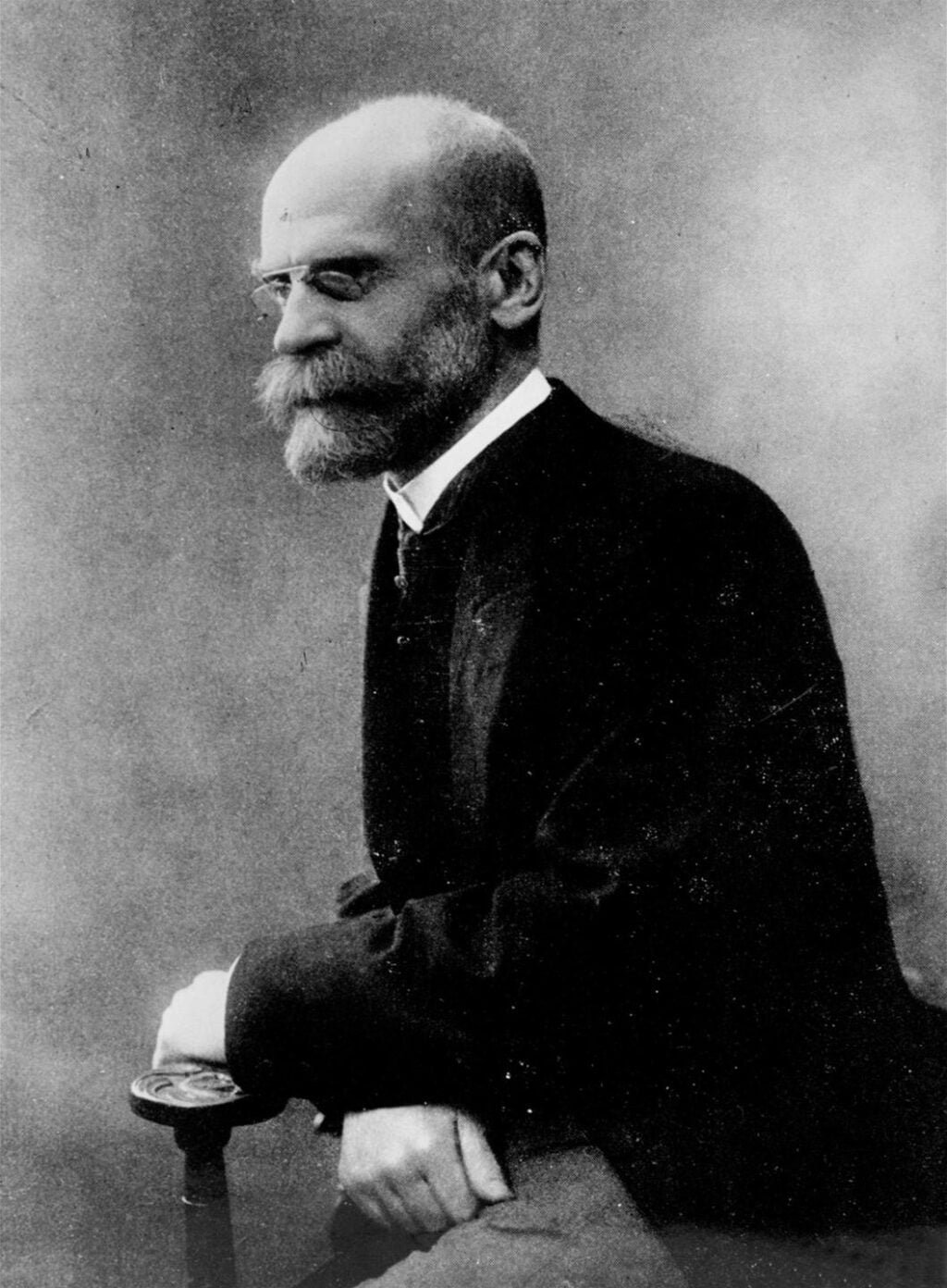
Emile Durkheim, often hailed as the father of sociology, played a pivotal role in shaping the course of sociological thought. This article takes you on an enlightening journey through Durkheim’s life and contributions, unraveling the enduring impact of his pioneering insights. From his groundbreaking theories to his enduring relevance, let us explore the legacy of the father of sociology.
1. Early Life and Intellectual Journey
Emile Durkheim was born in France in 1858. His fascination with human society led him to pursue studies in philosophy and sociology. Influenced by the social changes of the industrial revolution and the challenges of modernity, Durkheim sought to understand the fundamental principles that underlie social life.
2. The Sociological Method: An Analytical Approach
Durkheim emphasized the need for a distinct sociological method to study society scientifically. He believed that sociologists should adopt an analytical approach, using systematic observation and objective analysis to uncover the underlying social forces at play.
3. Division of Labor: The Social Glue
One of Durkheim’s seminal works was “The Division of Labor in Society,” where he explored the role of division of labor in maintaining social order. He argued that solidarity and social cohesion arise from the interdependence that results from different individuals and groups performing specialized tasks.
4. Collective Consciousness: Bonding the Community
Durkheim introduced the concept of “collective consciousness,” which refers to the shared beliefs, values, and norms that bind individuals in a society. He posited that collective consciousness contributes to social integration and regulates individual behavior.
5. Anomie: Understanding Social Pathology
Durkheim’s concept of “anomie” refers to a state of normlessness and social breakdown, often experienced during times of rapid social change. He recognized that excessive individualism and weakening social bonds could lead to social pathologies and moral disintegration.
6. Religion and Society: Rituals of Unity
In his seminal work “The Elementary Forms of Religious Life,” Durkheim examined the role of religion in society. He argued that religious rituals and practices create a sense of collective identity and foster social cohesion.
7. Contemporary Relevance of Durkheim’s Ideas
Durkheim’s contributions continue to resonate with sociologists today. His emphasis on empirical research, the study of social facts, and the importance of social integration remains central to the discipline of sociology. Moreover, his insights on social order, collective consciousness, and the impact of modernity continue to inform contemporary sociological theories.
The Enduring Influence
Emile Durkheim, the father of sociology, left an enduring legacy in the realm of social sciences. His pioneering insights continue to shape modern sociological thought, guiding us in the exploration of the complexities of human society and the quest for social harmony.