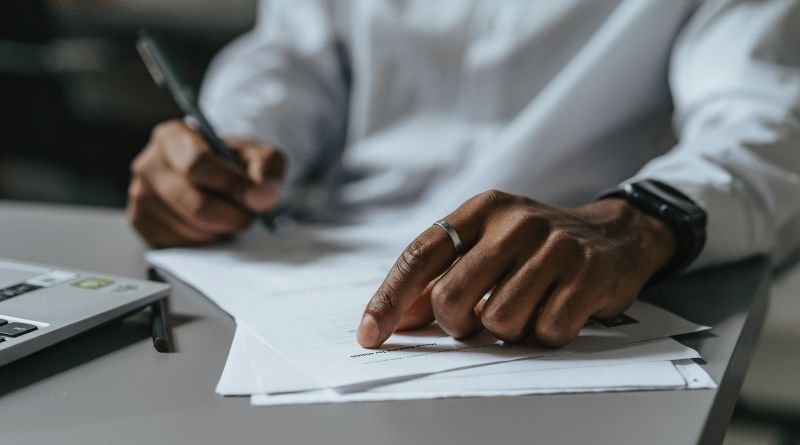
Living in a vibrant democracy like India comes with a crucial responsibility: knowing your rights. This knowledge empowers you to navigate life’s challenges, seek justice, and hold authorities accountable. While the Indian legal system is vast and complex, understanding fundamental laws and rights equips you to face everyday situations confidently.
1. Understanding the Bedrock: The Constitution of India
The cornerstone of every Indian’s rights is the Constitution, adopted in 1950. It enshrines six fundamental rights – right to equality, right to freedom, right against exploitation, right to freedom of religion, cultural and educational rights, and right to constitutional remedies. These rights form the foundation of individual liberties and protections against state overreach.
In 1997, the Vishaka case established the right to a safe workplace for women based on the right to equality and life with dignity. This landmark judgment highlights the power of understanding constitutional rights.
Familiarize yourself with the basic tenets of each fundamental right. Resources like the National Law Library and government websites offer simplified explanations and interpretations.
2. Safeguarding Your Dignity: Personal Rights and Laws
Right to Life and Personal Liberty (Article 21): This fundamental right guarantees protection against arbitrary arrest, torture, and deprivation of life and liberty. Understanding criminal codes and procedures empowers you to defend these rights effectively.
Right to Education (Article 21A): Free and compulsory education for children (6-14 years) is a fundamental right. Knowing this empowers you to advocate for your child’s education and hold authorities accountable for its provision.
Right against Discrimination (Article 15): Discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth is prohibited. Knowing anti-discrimination laws and legal recourse options equips you to challenge discriminatory practices.
Right to Information (RTI Act, 2005): This powerful law empowers citizens to access information held by public authorities. Knowing how to file RTI applications allows you to seek transparency and hold public bodies accountable.
In 2013, Aruna Shanbaug’s case, where the right to life with dignity was upheld, highlighted the importance of understanding personal rights and legal avenues for seeking justice.
Explore resources like the National Human Rights Commission website and citizen awareness campaigns to delve deeper into specific personal rights and associated laws.
3. Navigating Public Interactions: Laws for Everyday Situations
Consumer Protection Act, 1986: This law safeguards consumers against unfair trade practices, defective goods, and misleading advertisements. Understanding your consumer rights empowers you to make informed choices and seek redressal for grievances.
Motor Vehicles Act, 1988: Knowing traffic rules and regulations ensures your safety on the road and protects you from legal consequences. Familiarize yourself with driving licenses, vehicle registration, and traffic violation procedures.
Rent Control Laws: Renting a house? Understanding local rent control regulations, tenancy agreements, and eviction procedures protects your rights as a tenant.
Labor Laws: Every worker has rights to minimum wages, working hours, leave policies, and social security benefits. Knowing your labor rights empowers you to negotiate fair working conditions and seek legal recourse if needed.
The Minimum Wages Act protects millions of workers from exploitation. Knowing and asserting your rights under this law ensures fair compensation for your labor.
Research relevant laws based on your specific needs and situations. Government websites, legal aid organizations, and citizen awareness campaigns offer valuable resources and support.
4. Seeking Justice: Legal Resources and Support
Legal Aid: The Indian Constitution guarantees free legal aid to those who cannot afford it. Explore legal aid services offered by the government, bar councils, and NGOs to access legal representation and guidance.
Lok Adalats: These informal forums offer speedy and cost-effective dispute resolution for various matters. Understanding their jurisdiction and procedures can help you resolve legal issues efficiently.
Online Resources: Several government websites and legal information portals offer simplified explanations of laws, judicial procedures, and citizen rights. Utilize these resources to empower yourself with legal knowledge.
The Gram Nyayalayas Act provides accessible justice in rural areas through village courts. Knowing such alternative dispute resolution mechanisms empowers you to seek justice effectively.
Familiarize yourself with available legal aid options, Lok Adalats in your area, and reliable online legal resources. Remember, knowledge is power, and legal awareness empowers you to navigate life’s challenges with confidence.